Real-Time News Summary Platform

Introduction
This is our final project for the course “Web Application Programming.”
For the original source code, please visit GitHub.
Collaborators
Po-Cheng Huang, Yu-Yang Su, Chun-Han Lin, Chih-Chieh Yu, Fan-Jia (Hubert) Huang
Project Objectives
Provide Daily News Summaries
Use LLM technologies and web scraping systems to automatically collect and filter the most important news from major news sources daily. These are then converted into concise and clear summaries, allowing users to quickly grasp key information and save time.
Design an Intuitive and User-Friendly Interface
Develop a simple yet engaging web design that enables users to easily browse daily news summaries. The interface should feature good readability and offer clear categorization of news types to enhance the user experience.
Support Personalized News Selection
Allow users to customize their news preferences based on personal interests and needs. Users can select specific news categories (e.g., international, technology, finance) to access content more relevant to their interests.
Provide Full News Links and Detailed Information
Besides summaries, users who wish to dive deeper into specific topics can access original news links for full reports.
Enhance Information Absorption and Understanding Efficiency
Through efficient filtering and summary generation, help users quickly understand significant news, improving their awareness and responsiveness to daily events—ideal for busy individuals with limited time.
System Architecture
The project is divided into two main components: frontend and backend.
The backend is further split into Server, Web scraper, and AI API modules. The frontend is built using the React framework, while the backend uses Python for its web scraping capabilities.
The following provides a brief introduction to the functions of each part of the program:
Frontend UI
When the application is launched, React renders the main program App.js at the root location of the index.html page. The App.js file divides the page into several components, including Header, Sidebar, MainContent, and Footer, which together form the entire interface.
Users can click the hamburger menu to toggle the visibility of the sidebar and select categories from the menu to trigger API requests, which display the corresponding news content.
The styles for each component are stored in their respective CSS files for easier management, while static assets (such as icons and images) are sourced from the public folder and used directly in the application.
Backend Server
First, the necessary functions from other backend components are imported, and then Flask is used to initialize and run the backend server. When the frontend sends a GET request to fetch news data, the get_news() function checks if the requested news category has been scraped within the past hour.
# API route to get news data
@app.route('/api/news', methods=['GET'])
def get_news():
# Get the category parameter from the request
category = request.args.get('category')
global news_data, fetch_time
# Attempt to load existing data and fetch time from JSON files
try:
with open('./news_data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
news_data = json.load(f)
with open('./fetch_time.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
fetch_time = json.load(f)
except Exception:
pass
# Check if data for the category was fetched within the last hour
if category in fetch_time and datetime.datetime.strptime(fetch_time[category], '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') > datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(hours=1):
print('data passed')
return jsonify(news_data[category]) # Return cached data
else:
# Reload the news data for the category
load_news(category)
if category in news_data:
# Save updated news data and fetch time to JSON files
with open('./news_data.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(news_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
fetch_time[category] = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
with open('./fetch_time.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(fetch_time, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print('data passed')
return jsonify(news_data[category]) # Return updated data
else:
# If the category is not found, return an error response
print('data passed')
return jsonify({"error": "Category not found"}), 404
- If the data exists, it directly returns the cached news.
- If not, it sets the scrape time for that news category to the current time and calls
load_news().
# Function to load news data for a specific category
def load_news(target=""):
global news_data
# Scrape news data from ETtoday and CNA based on the target category
crawl_ettoday(target=target)
crawl_cna(target=target)
# Load ETtoday news data from the JSON file
with open('./ettoday_news.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
additional_news_data = json.load(f)
for key, value in additional_news_data.items():
news_data[key] = value
# Load CNA news data from the JSON file
with open('./cna_news.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
additional_news_data = json.load(f)
for key, value in additional_news_data.items():
# Merge data if the category already exists in `news_data`
if key in news_data:
news_data[key].extend(value)
else:
news_data[key] = value
# Generate summaries for all articles in the target category concurrently
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
try:
results = list(
executor.map(
get_summary,
[news['url'] for news in news_data[target]], # URLs of news articles
[news['title'] for news in news_data[target]], # Titles of news articles
[news['content'] for news in news_data[target]] # Content of news articles
)
)
except Exception:
return
# Update news data with the summarized title and content
for result in results:
url, title, article = result
for news in news_data[target]:
if news['url'] == url:
news['title'] = title
news['content'] = article
break
The load_news() function executes a web scraper to gather news data and uses multithreading to concurrently generate summaries for multiple news articles. Finally, the get_news() function sends the processed data back to the frontend. For more details, refer to the backend.py file.
Backend Web Scraper – the Central News Agency(CNA)
First, use the requests library to send an HTTP request to the CNA homepage URL (https://www.cna.com.tw). To prevent the website from blocking the scraper, include parameters in the headers and use fake_useragent to change the User-Agent with each request. This avoids reusing previously blocked User-Agents and ensures successful retrieval of valid responses.
Next, use chardet to detect and decode the encoding, and then parse the content using the BeautifulSoup library to extract the URLs of news category pages, storing them in the list cat_hrefs.
Then, iterate through the URLs in cat_hrefs, sending HTTP requests to each category page as described in step 1. Parse each category page to extract the URLs of the five most recent news articles, storing them in the list news_hrefs.
For each news article, send a request using the URLs in news_hrefs, retrieve the response, and parse each article’s category, title, content, and URL. Store this data in the dictionary news_contents.
Finally, after all content has been scraped, convert news_contents into a unified JSON format and send it to the backend for processing. This treats the scraper as an API that, when given parameters (such as the number of articles to scrape for each category), returns a standardized JSON response.
Backend Web Scraper – ETtoday
First, define the scraping function crawl_ettoday(article_limit), where the article_limit parameter is used to control the number of articles to be scraped, facilitating future team collaboration and adjustments.
Next, set the basic parameters:
url = "https://www.ettoday.net/news/news-list.htm": The ETtoday news list page URL.user_agents = [ ... ]: A list of User-Agent strings to simulate requests from different devices and browsers.headers = {"user-agent": random.choice(user_agents)}: Randomly select a User-Agent.
Then, use requests.get to send an HTTP request to the URL ("https://www.ettoday.net/news/news-list.htm") and use randomized headers to avoid being blocked and obtain a valid response.
Next, parse the HTML content using the BeautifulSoup library and select the news list section (class="part_list_2"):
- Title (
title_list): Content from<a>tags. - Category (
category_list): Content from<em>tags. - Link (
link_list): Relative paths to articles.
Then, iterate through the link_list, sending HTTP requests to each article URL, and scrape the content within the .story class (the class for the article body).
Next, extract paragraph content:
find_all("p"): Find all<p>tags, as each paragraph is usually wrapped in these tags.get_text(strip=True): Extract the plain text of each paragraph, withstrip=Trueto remove extra whitespace at the start and end."\n".join(paragraphs): Combine paragraphs into a single string, with each paragraph separated by a newline to maintain the original structure and readability.
Finally, categorize the scraped content into news_dict and use json.dump to convert the dictionary into a JSON file for output.
Backend LLM (Large Language Model) API
Using the OpenAI library, the system sends a prompt that specifies the desired output format along with the news title and content to be summarized. The API processes this request and returns a response. The returned content is then processed using functions like strip() and split() to convert it into the desired Python format. For more details, refer to the code in api.py.
Workflow
The overall platform operates as illustrated:
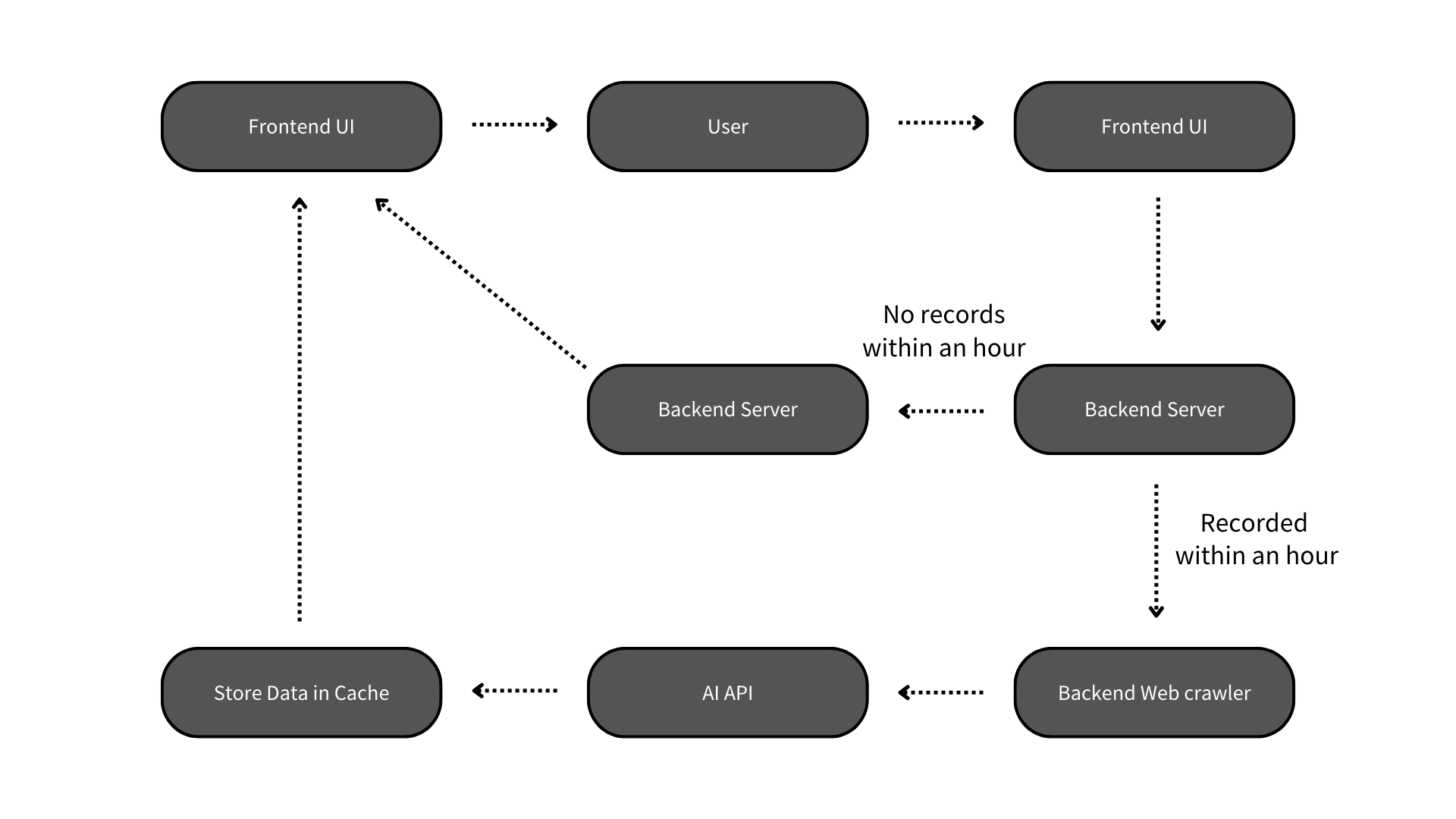
When a user accesses the platform via the frontend, the system checks if there are web scraping records from the past hour.
If records exist within the past hour, the system considers the news data sufficiently up-to-date and directly retrieves the stored web scraping ing data from the backend server to display it on the frontend.
If no records exist within the past hour, the backend performs real-time web scraping to collect the latest news data. This data is then processed using LLM to generate summaries, which are stored for future use and subsequently displayed on the frontend.
This design was implemented because real-time web scraping takes longer than initially anticipated. To avoid prolonged loading times during user interaction, we introduced this mechanism to balance efficiency and responsiveness.
Usage Instructions and Demonstration
Please follow these steps to run the program:
- Navigate to the
frontendfolder and executenpm installin the terminal. - In the
frontendfolder, executenpm startin the terminal. - Navigate to the
backendfolder and run thebackend.pyfile in the terminal.
Next, you will see the webpage displayed as shown in the illustration:

On the side, there are different news categories:

When you select a category, the webpage will display several real-time news summaries for that category:

Project Summary
This project integrates web scraping, artificial intelligence, and a minimalist frontend design to provide quickly generated and categorized news summaries, enhancing user reading efficiency and experience.
The project required a high degree of collaboration, with frequent communication between the frontend and backend teams to ensure smooth data transmission. I am thrilled to have successfully completed this project with my teammates and am deeply grateful for everyone’s teamwork, which made the success of this project possible.